Natural Henna Hair Dye vs Chemical Hair Dye - How They Work

How Henna’s Quality is Determined and Graded
June 1, 2018It is common today among both men and women to dye their hair to change their natural hair colors or cover their white or gray hair. Hair dyeing is thus one of the key services provided by hair salons to their customers to help them become more confident with a fashion statement or a younger look.
To know how hair dye works, view the video below for a quick explanation. For those who prefer to read and want to find out more about the 100% natural Herbriller hair dye, read on.
The Three Types of Hair Dyes
There are three types of hair dyes – temporary, semi-permanent and permanent – and they color hair differently. Hair salons generally use semi-permanent or permanent hair dyes, both of which contain a range of chemical ingredients.
Before we look at how the different types of hair dyes work, let us first have a look at hair structure.
Each strand of hair, or hair shaft, comprises three layers:
- medulla, the innermost layer;
- cortex, the middle layer which contains keratin (proteins) and melanin which gives natural color to our hair; and
- cuticle, the outermost layer with overlapping scale-like cells that protect the hair’s inner structure.
How Chemical Hair Dye Works
With temporary hair dyes, they simply stick to the cuticle like a coat of paint. Hence, the color generally lasts for 1 to 2 washings.
Semi-permanent hair dyes have molecule pigments that are small enough to slip between the scale-like cells of the cuticle and stick to the cortex. The color typically fades after 5 to 10 washings.
Permanent hair dyes cause lasting chemical changes to the hair and the color change lasts until the hair grows out or falls out. With permanent hair dyes, a chemical such as ammonia or a gentler substitute is used to open the scale-like cells of the cuticle. Another chemical called the developer is then used to stripe the natural hair color off the melanin and kick off chemical reactions that oxidizes and deposits the new color into the hair cuticle. The chemical dye resists multiple washes and the color does not fade. While color retention is good, the cuticles are damaged and moisture in the hair is reduced, resulting in dry, damaged hair.
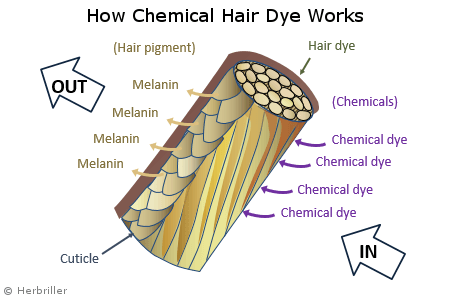
How chemical hair dyes work
How Natural Henna Hair Dye Works
Henna itself contains a natural red coloring component, called lawsone. When used to dye hair, the henna paste coats the hair shaft and lawsone gradually migrates from the henna into the hair shaft through gaps in the cuticle, then binds with keratin and strengthens the cuticle. This results in naturally colored hair. With repeated use, the color of the hair settles and deepens.
The strength of the hair is increased, and the moisture retention capacity of the hair is also strengthened. Additionally, scalp condition improves, decreasing hair loss and dandruff. The coating of henna on the surface protects hair from UV rays and pollution, resulting in healthy and shiny hair overall.
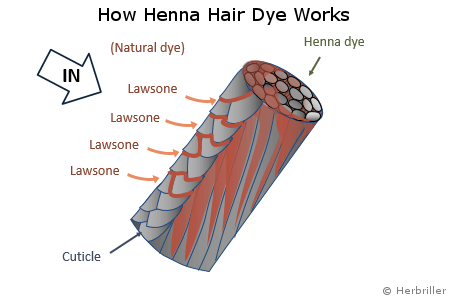
How henna hair dyes work
Herbriller covers white and gray hair using henna (and its lawsone coloring component) as one of its 100% natural ingredients. For customers looking for something different from the orange color from lawsone, Herbriller has a range of colors that contain other natural color dyes such as indigo to achieve different shades of brown for the hair.
Differences Between Natural Henna and Chemical Hair Dyes
Here is a summary of the main differences between henna and chemical hair dyes:
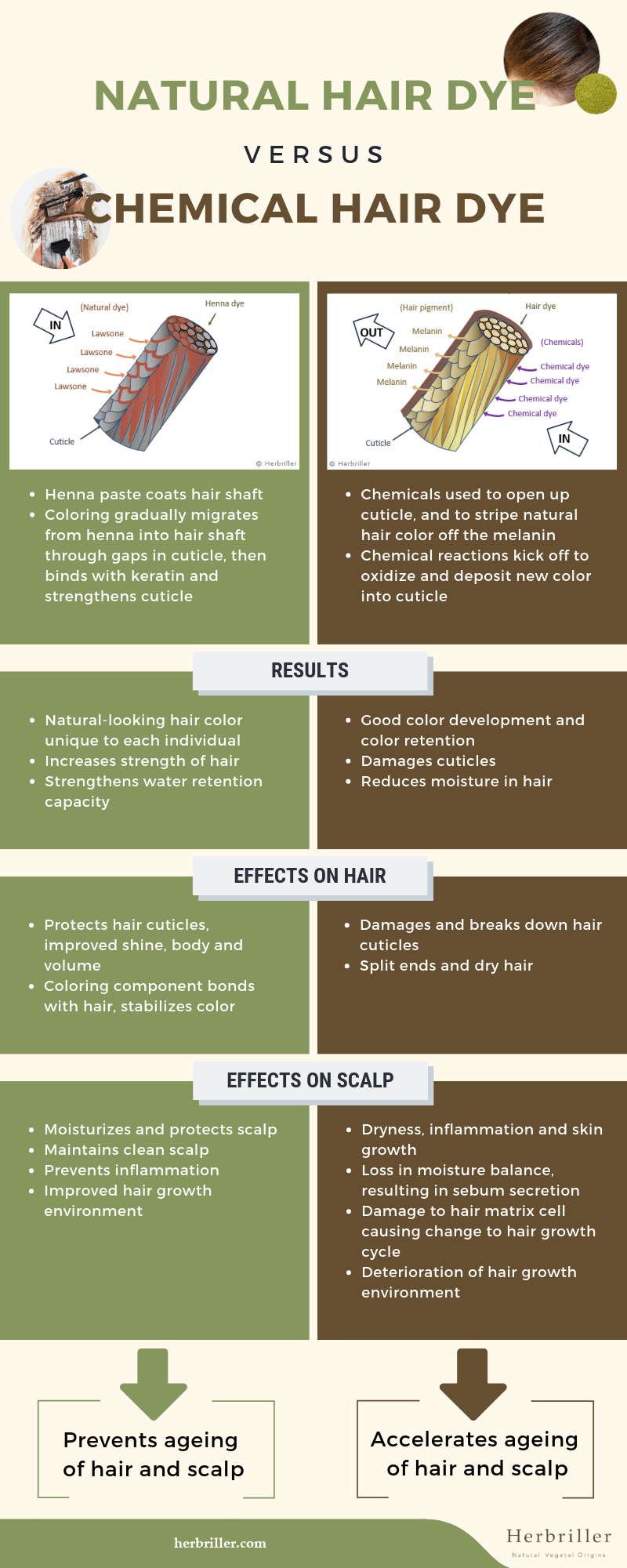
Infographics: Natural henna hair dye versus chemical hair dye
| Effects | Henna Hair Dye | Chemical Hair Dye |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
| On Hair |
|
|
| On Scalp | Henna component
|
Chemical stimulus induces
|
| Overall | Prevents ageing of hair and scalp | Accelerates ageing of hair and scalp |
While chemical hair dyes provide good color retention, the way that chemical hair dyes penetrate the hair shaft to color the hair causes damage and accelerates the ageing of both the hair and scalp. Natural henna hair dye, on the other hand, prevents ageing of the hair and scalp as it improves the condition of the hair and scalp with its medicinal properties while naturally coloring the hair.
Takeaway
Whether you are a hair salon owner providing hair dyeing services or a salon customer going for hair dyeing services to cover your white hair or change your hair color, use this information on how natural henna and chemical hair dyes work to help you make a choice on the hair products to use.
